What is Lipoma ?
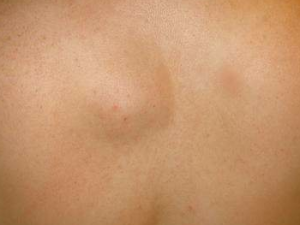
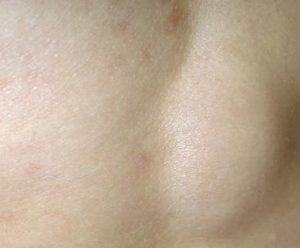
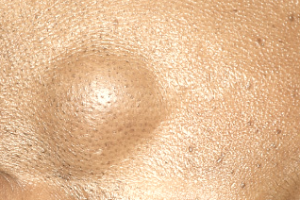
It refers to a non-cancerous additional growth of fat cells occurring in the space between the skin and the layer of muscle present just below. Lipoma is a non-malignant development of soft tissues, which have an appearance similar to a fibrous capsule. It is a fatty bump with a tendency to grow slowly. It feels doughy to touch and can be easily moved with the fingers.
Lipoma can affect people of all ages and genders. However, it is more commonly observed in individuals who are in the age group ranging from forty to sixty years. The rate of incidence for lipoma is one in 100. It is normal to detect the presence of one or two growths of lipoma in people within the above mentioned age group. However, it may be noted that some individuals have a genetic predisposition to develop many such soft tissue development across the body.
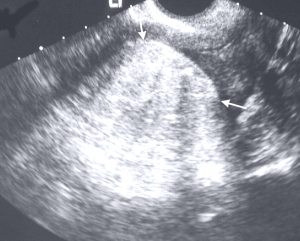
In some instances, lipoma can grow within the body as well. Since they do not result in any problems, they often stay undetected. However, as per the location of the internal lipoma, a few can be harmful. For example, a lipoma affecting the gastrointestinal tract can result in ulcers, bleeding and painful blockage.
Lipoma in dogs
Lipoma can be found to occur in various animals, but commonly occurs in dogs, especially aged Doberman Pinschers, Labrador Retrievers and Miniature Schnauzers and female dogs that are overweight. Most overweight and older dogs have a minimum of one lipoma. The condition normally affects the upper limbs and trunk of dogs.
Lipoma Symptoms
- Lipoma is not cancerous and is more likely to be not dangerous. Hence treatment is often not needed. The condition can be present as a single or several growths.
- The condition normally affects the neck, shoulders, arms, abdomen, back and thighs. It is typically small in size and less than 5 centimeters, but can grow bigger
- In rare cases, clusters of fat cells come together below the skin and develop into multiple fatty bumps. It generally occurs due to genetic causes and the disorder tends to be passed down through the generations. Reoccurrence of deeper lipoma is also common.
- When one experiences constant growth of a lipoma, or results in pain due to its location or leads to cosmetic ugliness and damage, then it can be readily removed via surgery.
- If a lipoma develops and press the adjacent nerves, then it can be painful
It is essential to note that even though lipoma does not result in medical complications, it is best to seek medical attention when one observes the development of a bump on the skin.
Types of lipoma
The different types of lipoma are as follows:
- Chondroid lipomas: They are solid, deep rooted, yellowish growths that are typically present in a woman’s legs
- Angiolipoleiomyoma: It is an attained, acral, solitary nodule that does not elicit any symptoms. It develops as a combination of fat, smooth muscle cells, blood vessels and connective tissues.
- Intradermal spindle cell lipoma: It can be found affecting the trunk, neck, head, and lower and upper extremities. It typically occurs in women and is widespread.
- Angiolipoma: It is a subcutaneous and painful tumor that has all the characteristics of a lipoma
- Hibernoma: It is made of brown fat
- Corpus callosum lipoma: It is an uncommon congenital anomaly, featuring growths that are comparatively smaller measuring one to 3 centimeters in diameter, but which can grow larger up to 10 to 20 centimeters and can be as heavy as four to five kilograms.
- Neural fibrolipoma: It refers to an overdevelopment of fibro-fatty tissue alongside a nerve trunk and often resulting in compression of the nerve
- Pleomorphic lipomas: It mostly affect the back and neck and commonly occurs in older men
- Superficial subcutaneous lipoma: It grows just under the skin and is the most common form of lipoma. It can affect any area of the body that contains fat. However, some of the common body regions that are prone to developing this type of lipoma are the forearms, trunk and thighs.
- Spindle-cell lipoma: It is a slow developing, subcutaneous, asymptomatic growth which mainly occurs in the back, neck and shoulders of older men.
Lipoma Causes
- The precise cause of lipoma is not known. However, lipoma has a tendency to be passed down in families. Thus, one can safely deduce that inherited factors have an important role in the growth and occurrence of lipoma
- A minor trauma can trigger the onset of lipoma. In most cases, being overweight or obesity does not result in development of lipoma.
Some of the risk factors that increase the vulnerability to developing lipomas are listed below:
- Individuals affected by Gardner’s syndrome, Madelung disease, adiposis dolorosa and Cowden syndrome are at greater risk to lipoma
- Lipoma is uncommon in children and typically tends to occur in middle aged individuals who are between the age group of 40 to 60 years
- Adiposis dolorosa is a type of lipoma that is normally found to occur in post-menopausal, obese women. They cause exhaustion and swelling
- Benign symmetric lipomatosis can be commonly detected in men who have been chronic alcoholics, but can occur in others as well.
Lipoma Treatment
Some of the treatment methods for lipoma are as under:
- Steroid injections: This procedure can be used to contract the lipoma. However, this treatment method does not result in complete lipoma removal
- Surgery: Surgery involves the removal of lipomas by means of a simple excision. The procedure takes less than thirty minutes and is generally carried out under local anesthesia. Surgical removal of lipomas rarely results in a reoccurrence
- Liposuction: This procedure may be used if the lipoma has a tiny connective tissue component and is soft. It involves the use of a needle and syringe to aid the process of fatty lump removal. It normally causes less scarring. However, this option may not result in complete removal of larger lipomas, thereby increasing the risk of recurrence
Recovery from lipoma treatment: Lipomas are generally harmless and most types do not result in health complications. However, if they occur deeper in the internal organs, it can be dangerous. Also, deeper lipomas are prone to recurrence as their complete removal via surgery is not always possible. Lipoma cases rarely get transformed into cancerous liposarcomas.
Lipoma Pictures
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself
or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find
out where u got this from. many thanks