Postmenopausal osteoporosis, or primary type 1 osteoporosis, is a common disease for women who have reached past the menopausal stage. Osteoporosis is a bone disease that increases the person’s risk to bone fractures.
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease that is four times more common in women than in men. This type of disease weakens the bones, exposing it to risk of bone fractures. Bone fractures are usually common around the wrist, hip and spine area. And they may vary from mild to severe or to very painful fractures. Osteoporosis is a lifelong condition that can be reversed through correct treatment.
What are the Causes of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis?
The main causes of postmenopausal osteoporosis that cannot be avoided are advanced age, family history, being a female and has reached or past the menopausal stage. Other causes that can be avoided are poor diet, inactivity, smoking and high alcohol intake. Other medical-related causes of osteoporosis are prolonged exposure to steroid drugs, early menopausal especially under 45 years old, hormone abnormalities, kidney disease and Vitamin D deficiency.
What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis?
At the early stages of osteoporosis, there is usually no sign or symptom manifested. But once the bones are weakened due to osteoporosis, the symptoms experienced are:
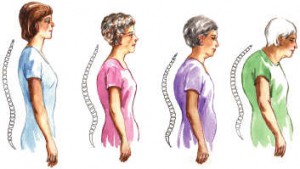
• Back pain
• Stooped posture
• Fracture in the vertebra, hip, wrist and other bone parts
• Decrease in height
Treatment for Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women
Medications for osteoporosis
• Raloxifene – this medication is beneficial for postmenopausal women for it has no estrogen-related side effects which may lead to uterine cancer and breast cancer.
• Calcitonin – is a hormonal medicine produced by the thyroid gland that reduces bone resorption and also slows down bone loss. It can also be used as a pain relief and also prevent further fracture in the spine.
• Teriparatide – this drug is composed of parathyroid hormone that is most essential in treating postmenopausal osteoporosis. While other drugs prevent bone loss, this powerful drug stimulates bone growth. But up to now this drug is still under study with regards to its long term side effects.
Hormone Therapy for osteoporosis in post menopausal women
After menopause, estrogen is used to maintain bone density. However, this therapy also increases the risk of blood clots, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and heart disease. Because of its side effects, this type of treatment is not the doctor’s first choice of treatment.
Physical Therapy
Engaging in different physical activities is essential in treating postmenopausal osteoporosis. Regular exercise at least 30 minutes a day does not just increase bone strength but also improves posture and balance.
How to Prevent Osteoporosis?
There are many self care ways to prevent further damage brought by postmenopausal osteoporosis. These include regular exercise, eating more foods rich in calcium, taking Vitamin D, avoiding medications like steroids, limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking. Read about diet for osteoporosis prevention
It is normal that when a woman ages, her bone structure weakens and loses its strength. Often times, postmenopausal osteoporosis may progress without any warning until a weakened bone gets fractured and causes pain. When this happens, you’ll be at risk of having another fracture. Fortunately, many treatments are available to help stop any further bone damage but before that happens try to practice the aforementioned preventive measures.
I was just searching for this info for some time. After six hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your website. I wonder what’s the lack of Google strategy that don’t rank this kind of informative web sites in top of the list. Normally the top websites are full of garbage.