The spleen is a gland located in the abdomen. Across the 20th century, it was considered as a mystery organ, due to limited know-how about its functionality. The Greek doctors believed that the spleen played an important role in the manufacture of ‘black bile’, which according to them was one of ‘4 humors’ that preserved the balance of the body’s functions.
Increased manufacture of black bile was believed to result in depression or melancholia. The ancient Chinese medicine men believed that the organ was instrumental in maintaining will power and temperament. The current age doctors know about the spleen’s functions. It is considered as a component of the lymphatic system
Spleen is considered as one of the most vital organs of the body. It occurs in nearly all kinds of vertebrate animals. The name has its origins in the Greek word ‘splen.’ It is important to the immune system and performs the important function of supplying blood during emergencies as well as helping the body in the elimination of aged blood cells.
Location of spleen
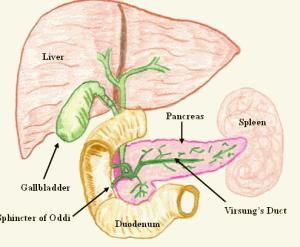
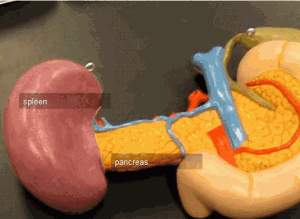
The spleen is an organ that does not come with a duct. It is really tiny and can be compared to a closed fist. It occurs in the upper left part of the abdominal cavity, just under the diaphragm and at the back of the stomach. One cannot see or feel it, because it is enclosed by the ribs. It is located close to the ninth, tenth and eleventh rib.
The spleen is enclosed in a capsule made of powerful connective tissues. This capsule comprises of two kinds of tissues, i.e. the white pulp and the red pulp. The white tissue consists of lymphoid tissue like lymphocytes plasma cells, and lymphatic nodules. The red pulp is composed of blood and performs the function of blood filtration. Both the forms of pulps occur in an even manner across the spleen. Each has a distinct set of functions. The blood flows into the spleen via the splenic artery.
Normal Spleen Size
When the spleen is normal, then it measures 7 x 5 x 2 inches in size. It size differs depending on the person. However, on an average, the adult organ is around four inches with an estimated weight of about 0.44 lbs.
Functions of the spleen
In addition to the white and red pulp, the spleen consists of lymphocytes or white blood cells, and macrophages. They aid in defense of the body against infections and also in disposal of foreign substances, dead tissues and other unnecessary matter from the bloodstream.
The different functions of each tissue type are discussed below:
- The red pulp is made of reticular fibers and blood. It carries out the important function of filtering blood of all the contaminations, dead cells and other unwanted, deteriorated matter.
- The white pulp is also referred to as malpighian bodies or lymphoid nodules of the spleen. They occur abundantly in lymphocytes and thus essential to functions of the immune system. These functions involve elimination of infected cells and protection of the body against such attacks. The spleen and other organs occurring in lymph nodes can identify attacks by viruses, bacteria and other pathogens and activate instantly to ward off their effects. The spleen manufactures lymphocytes that release antibodies which destroy the bacterial and viral cells. The infection is thus limited and later obliterated by the macrophages.
- The spleen does not have any special digestive roles. It stores blood and provides the extra blood required by the body in time of emergency, trauma or injury. Also, it stores iron in the form of ferratin which is acquired from dead blood cells, and later used by the bone marrow to produce red blood cells.
- Besides these, the spleen also performs several other functions. It produces red blood cells for the fetus, prior to delivery. Once the baby is born, red blood cells are manufactured by the bone marrow. Additional amounts of platelets are stored by the spleen, which are supplied for coagulation purposes when required. It also stores monocytes, a part of WBCs, which aid the healing of injured tissues.
- It may be noted that despite the many important functions performed by the spleen, it is not vital to human existence. If the spleen is removed due to tumors or other causes, then its functions are taken over by the liver and other organs.
Spleen Problems – Disorders
Some of the disorders associated with the spleen are as follows:
- Spleen enlargement may result from viral infections, liver diseases, blood cancers and other such abnormalities
- Storage of increased amounts of platelets can result in thrombocytopenia
- An injury may lead to immediate rupture of the spleen or it can occur a few weeks later. A burst spleen can result in severe internal bleeding which can be life-threatening
- The spleen can be affected by sickle cell anemia, a condition that causes obstruction of blood flow leading to organ damage
- Occasionally, people may have 2 spleens which can result in health problems
Enlarged spleen
- It can be caused by many reasons. It is not a serious condition, but an overactive enlarged spleen can lead to increased destruction of red blood cells.
- Enlargement of spleen may be caused due to viral and bacterial infections, inflammatory conditions, cancers, injuries and occurrence of cysts.
- Its symptoms include:
- Pain in upper left part of abdomen. Such pain may travel from the abdomen to the shoulders and back.
- Children may experience discomfort and fullness
- Inability to consume large quantities of food
- Weight loss and easy bleeding
- Elevated risk to jaundice and anemia
- Reduced ability to actively ward off infections
- Fatigue
- Treatment of an enlarged spleen includes
- Stoppage or restriction of physical activities to avoid aggravating the condition
- Medication therapy
- Surgical removal of spleen in severe cases
- Damage to the splenic capsule can cause the spleen to rupture. It can happen due to a heavy blow to the abdomen or chest area, from accidents, or from contact sports. An enlarged spleen is also prone to becoming ruptured.
- Its symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness of the upper left abdominal area. Such pain varies as per the severity of spleen rupture and can radiate to the shoulders
- Severe internal bleeding can cause the4 blood pressure to drop
- Paleness, confusion, restlessness, anxiety, blurred vision, lightheadedness and fainting are other associated symptoms
- Treatment of a ruptured spleen includes
- Hospitalization, wherein blood transfusion may be required to replenish the lost blood.
- Medications may be prescribed as per the seriousness of the condition
- Severe cases need surgical intervention
Ruptured spleen
Spleen anatomy pictures
Spot on with this write-up, I really assume this website wants way more consideration. I抣l most likely be again to read much more, thanks for that info.