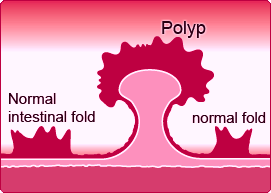
A polyp is any enlarged tissue that can be found in the mucous membrane such as in the linings of the nasal passages, urinary bladder, and intestinal tract. Polyps that develop along the linings of the small and large intestines are called intestinal polyps. It is an overgrown tissue that has different shapes and sizes and may grow with stalks and can also be flat.
What are Intestinal Polyps?
An intestinal polyp is a mass of tissue that has grown abnormally in the digestive system due to the rapid increase of the number of cells. The abnormal formation of mass tissue is known as neoplasm. Intestinal polyps develop in the linings of stomach, the small and large intestines. The linings in the stomach are responsible for food digestion. These overgrown tissues may develop during a person’s lifetime but most of them remain unnoticed since they cannot be felt in the digestive system. It can only be detected if the body undergoes autopsy. An estimated 30% of the population develops intestinal polyps at any stage of their lives and the chances of developing them will most likely happen as a person gets older. Some of these become malignant tumors and can cause cancer. Intestinal polyps that become malignant generally grow in the large intestine also known as the colon or large bowel. The possibility of a polyp turning into a malignant tumor depends on its location in the digestive system. Only 1% percent of the intestinal polyps become malignant.
Causes and Location of Intestinal Polyps
Around 95% of intestinal polyps develop mostly in the large intestine. Their growth may arise due to some hereditary diseases such as Gardner’s syndrome, Peutz-Jegher syndrome, Juvenile Polyposis, familial polyposis of the colon, Lynch syndrome and Turcot’s syndrome. The inheritance of these diseases are known as autosomal which means it is not sex related and can be acquired by the child either from his father or mother. It is during puberty that intestinal polyps appear in all of these hereditary diseases. Except for the Peutz-Jegher syndrome and Juvenile polyposis, the rest of the hereditary diseases have a high percentage where intestinal polyps will become malignant in the large intestine. This will happen when a person reaches the age of 40. A person diagnosed with these hereditary diseases should surgically remove the colon early in his adult life.
Polyps may also develop in the stomach along the linings but they are typically benign tumors. Polyps do not also possess a threat of becoming malignant but can be an obstruction when found in the small intestines. Polyps may grow large and will affect the movements in the small intestine. Polyps that are small can pull the part of the intestine during movement which are adjoined to the other intestinal section and may cause the inversion of one section of the intestine to the other. The inversion of one section to the other is called Intussusception.
Intestinal polyps that grow in the colon and become malignant are not only caused by hereditary diseases but also by diet. Based on known studies, animal fats contribute largely for the development of colon polyps. Other formation of polyps is due to the lack of fiber intake. Large polyps can cause obstruction in the intestine which leads to stomach or abdominal pain. If a colon polyp becomes malignant, signs of bleeding and changes in bowel movement can be observed.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Intestinal Polyps
When a person reaches the age of 40, there is a possibility that intestinal polyps may develop and at this age testing the stool for blood or colonoscopy should be conducted. In the stool test, a stool sample will be placed in a small cup and tested in the laboratory for signs of cancer like blood and changes in DNA. Colonoscopy is a procedure that lets the doctor examine the inner linings of the large intestine with an instrument called a colonoscope. Most of these polyps are found in the sigmoid colon which is the lower part of the colon. In colonoscopy, a medicine will be given by the doctor to sedate the patient and during the test the doctor will observe the whole colon by threading the colonoscope that has a camera which shows the images on the monitor. The colonoscope has a tool that can remove polyps. Usually the doctor removes the polyps during colonoscopy.
The other type of colonoscopy is the Computerized Tomography (CT) scan which is also called virtual colonoscopy. In this procedure, the doctor places a thin, flexible tube into the rectum with a machine built with x-rays and computers that makes pictures of the large intestine shown on the TV screen. Colonoscopy is a much longer procedure than CT scan because polyps are needed to be removed during the test.
Colonoscopy is similar to sigmoidoscopy. In sigmoidoscopy, the doctor places a thin, flexible tube called sigmoidoscope into the rectum. Only one third of the last part of the colon can be observed by the doctor using sigmoidoscope.
Another type of test to determine the presence of intestinal polyps is the Barium enema. In this test the doctor puts the barium which is a liquid into the rectum. After this, x-ray imaging is used to look for polyps in the large intestine. Barium is a white substance which makes the large intestine white in appearance in the film and makes the polyps distinguishable since they are dark in appearance.
Prevention of Intestinal Polyps
In order to prevent polyps from becoming cancerous, patients with the aforementioned hereditary diseases should undergo surgical removal of all or part of the colon. This procedure is called colectomy. Children whose parents have hereditary diseases should be examined early in their adult life since probably around half of them will experience the same disease. And for the majority of the population, proper diet should be observed such as decreasing the amount of fat and increasing fiber intake to prevent cancer polyps.
Doctors are not yet able to find a real solution to stop intestinal polyps. The most realistic thing that could be done to avoid the risk of getting them is to stop smoking, avoid alcohol, eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, eat less fatty foods, and eat foods that contain calcium such cheese and yogurt.